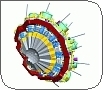
SAGE
SAGE is a Silicon And GErmanium spectrometer to perform simultaneous electron and γ-ray and spectroscopy.
"How many protons and neutrons can be assembled to form the heaviest nuclei?"
This fundamental question has been at the heart of nuclear structure physics for several decades.
Today, spectroscopic techniques can finally be brought to bear. In heavy and highly charged nuclei internal conversion starts to compete strongly with the main energy dissipation process that is the gamma emission. When studied separately, both types of radiation can only reveal a partial picture of the nuclei properties.
SAGE has been designed to offers the unique possibility to perform simultaneous electron and g-ray spectroscopy in order to provide a much better insight into how nuclear shapes and properties of valence nucleons can bind the heaviest nuclear systems.
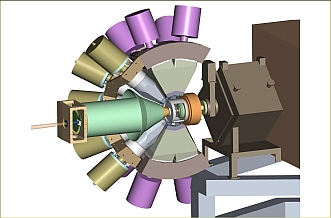
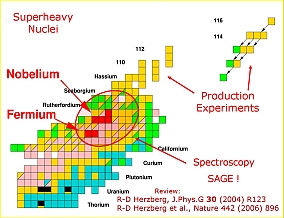
Odd nuclei such as 251Md, 255Lr and 253No will reveal the single particle configurations close to the “Island of Stability” in great detail providing much-needed guidance for theory.
Main features of SAGE:
- Highly segmented (100 Pixel) Si detector 1 mm thick.
- Near-180° geometry for superior energy resolution.
- 100 Digitally instrumented channels @ 50 kHz.
- High electron efficiency – avoid bottleneck.
- Full integration into triggerless TDR data acquisition.
- JUROGAM II for Ge efficiency (5.8%).
- Full integration with RITU and GREAT for recoil-decay tagging studies.
- 10 - 50 kV HV barrier to suppress d electrons.
- Fully STFC funded.
More information on SAGE can be
found at http://ns.ph.liv.ac.uk/~rdh/sage2.htm
Contacts